Efficient recycling of lithium-ion batteries
Innovative technology for a sustainable circular economy.
Electromobility is revolutionizing the way we get around. How- ever, as the number of electric vehicles increases, so does the challenge of recycling their batteries in an environmentally friendly way at the end of their service life. Conventional recycling methods often reach their limits here, as lithium-ion batteries from electric cars are large, heavy and contain valuable raw materials. Our innovative recycling plant offers a sustaina- ble and economical solution for safely and efficiently processing batteries with dimensions of up to 2,000 mm in length and a unit weight of up to 900 kg.
Resource-saving process - ecological and economical
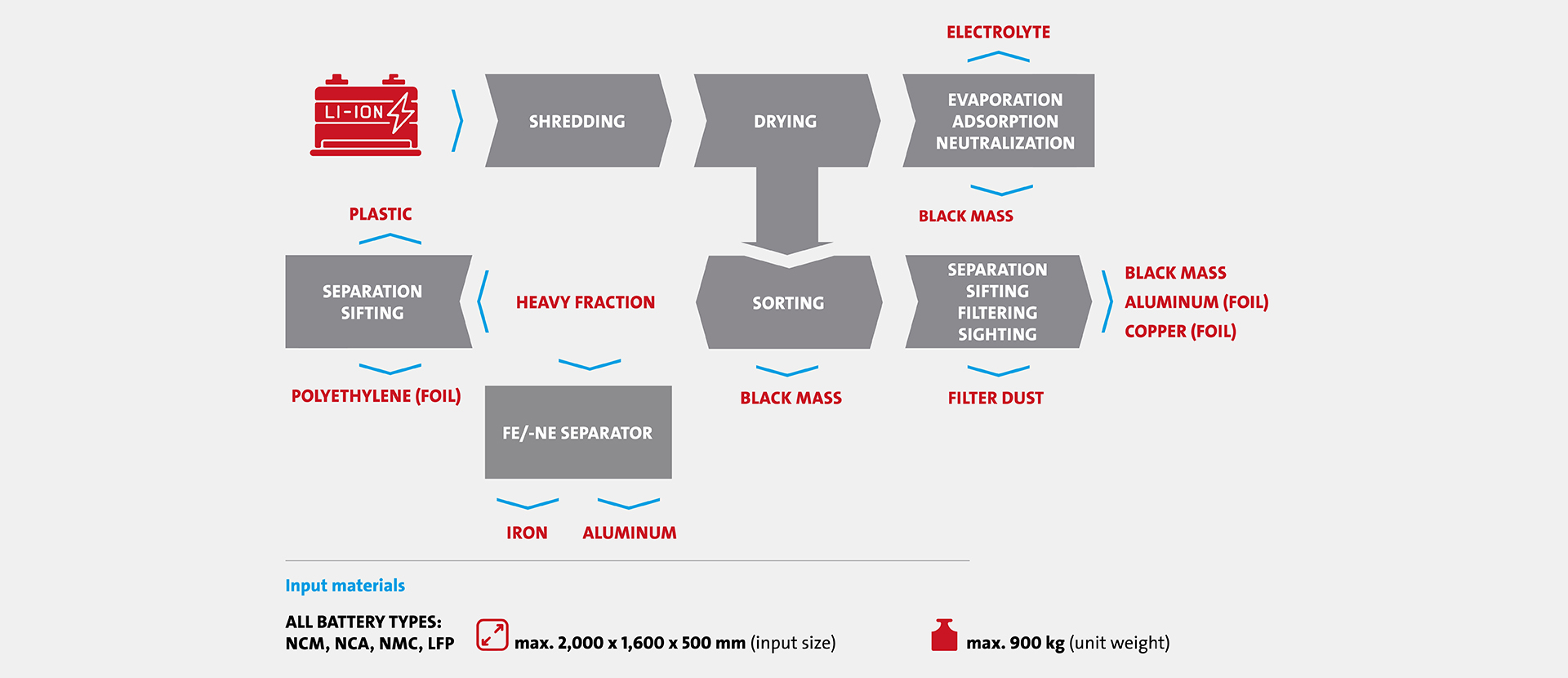
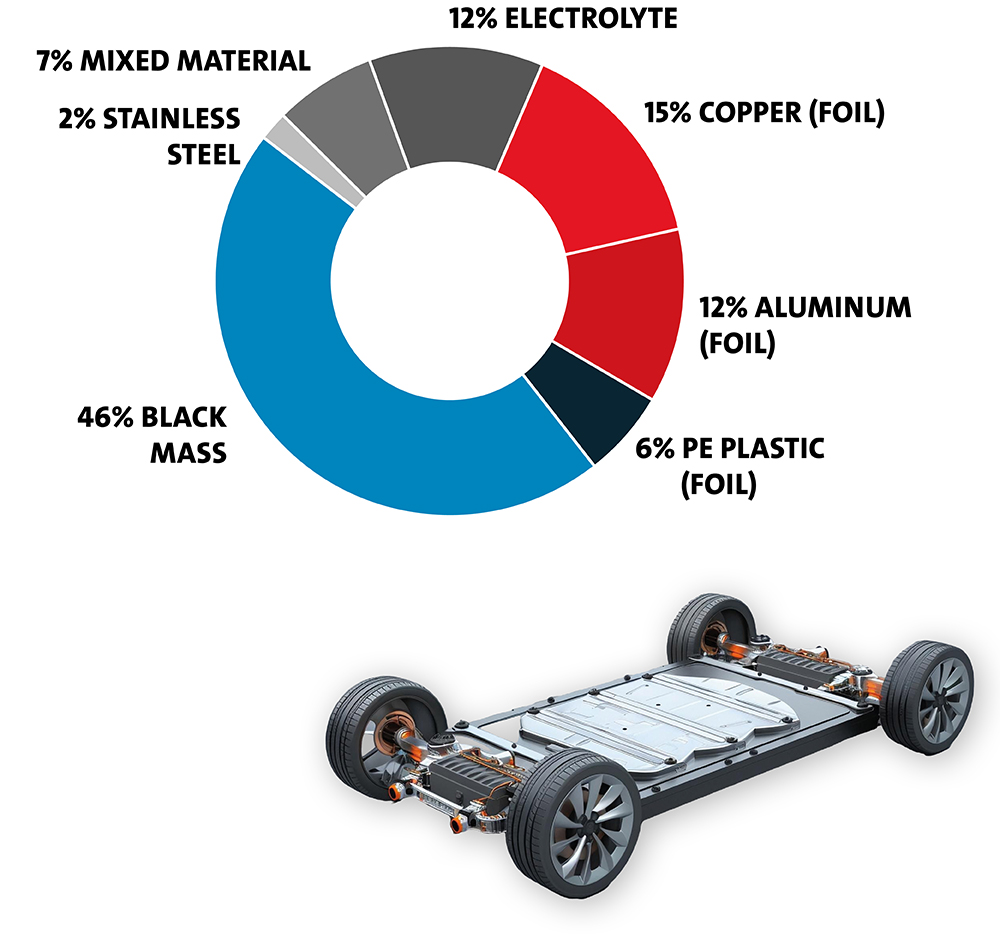
Lithium, cobalt, manganese and copper are essential raw materi- als for modern energy storage systems. However, their extraction is associated with considerable environmental and social chal- lenges. An efficient recycling process helps to recover valuable materials and conserve natural resources. Our technology makes it possible to process used batteries completely mechanically - by shredding, classifying, sorting and targeted evaporation of the volatile electrolyte components and subsequent re-liquefaction. The result: a safe, economical and sustainable solution for the recycling of valuable raw materials.
State-of-the-art technology for maximum efficiency
Our multi-stage recycling process ensures optimum recovery of the raw materials contained in the batteries. The individual work steps - from safe discharge and mechanical shredding to precise separation and recondensation - have been specifically designed to maximize efficiency and environmental protection in equal measure.
Safe discharge: First, the residual energy remaining in the battery is reduced in a controlled manner to avoid potential risks such as short circuits or thermal reactions.
Mechanical shredding: The batteries are shredded in a specially designed process to ensure optimum material separation.
Drying & recondensation: The volatile electrolyte components are vaporized and then recondensed.
Precise separation process: Sifting, screening and classifying processes are used to cleanly separate the individual materials such as aluminum, plastics and copper.
Recovery of the “black mass”: This contains the valuable coating materials of the electrodes, including lithium, cobalt and man- ganese.
With our state-of-the-art recycling technology, we are setting new standards in the sustainable recycling of lithium-ion batteries. Efficient, safe and forward-looking - for an environmentally friendly circular economy.
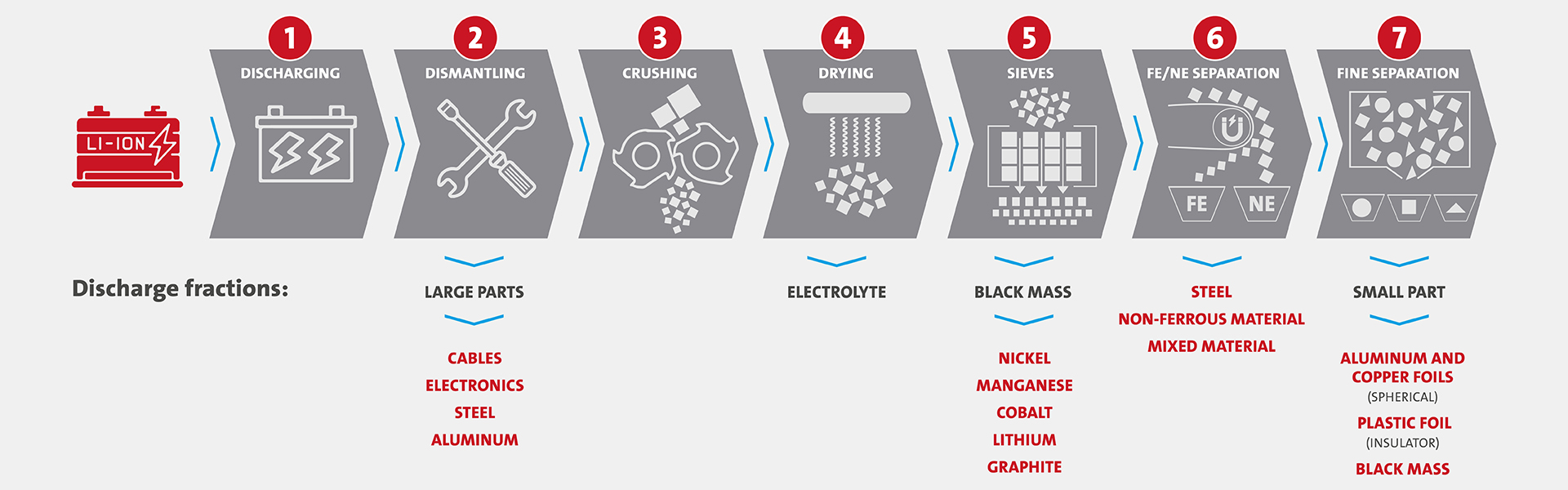
- Loading the modules and packs onto lifting work tables for ergonomic pre-assembly
- Checking the batteries by specialists for residual voltage and, if necessary, discharging them to 0volts (maximizing fire safety)
- Disassembly of cables, plugs and solid parts
- Transfer of the prepared batteries via the feed roller conveyor to the fully automated recycling process
- Batteries and accumulators are fed into the inert system via an airlock
- Inerting is carried out by nitrogen system operation from an oxygen content of < 3% in the entire inerting system (monitored by oxygen sensors)
- The first stage of shredding takes place via a twin-shaft shredder with a final piece size of 50 x 100-150 mm
- The material is then conveyed for secondary shredding and shredded to a determinable particle size
- Drying takes place in discontinuous vacuum operation
- An agitator in the vacuum dryer prevents the material from caking
- The dried shredded material is fed into an air separator, which separates light and heavy material
- The light material, mainly consisting of plastic, aluminum/ copper foils and black mass, finds its place in the buffer container after being finely shredded again
- The heavy material is discharged separately to separate ferrous metals and non-ferrous metals from mixed materials, such as internal wiring and coarse plastics
- For further processing, the material is fed from the buffer container to a sifting machine
- The screened fine fraction consists of black mass and is filled into BIG BAGS
- The coarser fraction, consisting of mixed plastic/aluminum/ copper foils, gets finely in a rounding mill
- In a last sifting machine combined with air separation unit the plastic films, the rounded aluminium/copper foils, and the remining black mass get separated
- An additional air separation unit allows the separation of rounded aluminium and copper foils